1 How generative AI works
What is generative AI?
Generative Artificial Intelligence, or generative AI, is a class of computer algorithms able to create digital content – including text, images, video, music and computer code. They work by deriving patterns from large sets of training data that become encoded into predictive mathematical models, a process commonly referred to as ‘learning’. Generative AI models do not constantly refer back to the data they were trained on, but rather generate novel content entirely from the patterns they encode. People can then use interfaces like RMIT’s Val, ChatGPT or Adobe Firefly to input prompts – typically instructions in plain language – to make generative AI models produce new content.
As the development of practical and high-quality generative AI emerges, it can become a helpful tool for our everyday work and has the potential for diverse applications such as art, writing, and software development.
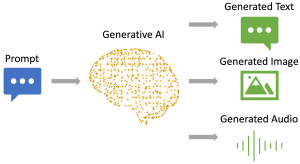
“Generative AI” by University of Sydney is licensed under CC BY NC 4.0
The core of a generative AI tool is a trained deep-learning model that generates text, an image, or other media in a human-like fashion based on a given user input, i.e. prompt. This model is trained on massive amounts of data to learn from patterns in the data. For example, it would learn that certain words tend to follow others, or that certain phrases are more common in certain contexts. The model uses the prompt to produce a completion, which is then presented back to users.

Image by University of Sydney is licensed under CC BY NC 4.0
The quality of the generated output depends on several factors, including the amount and quality of the training data, the prompt’s complexity, and the model’s size. Larger models usually generate better outputs, but require more computing power and resources.

