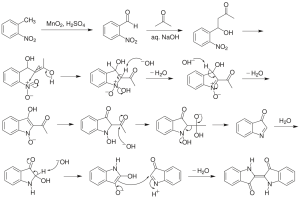
3.7 Organic Reactions
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Recognise characteristic chemical reactivity patterns associated with different families of organic compounds
We have learned that the properties of organic substances can be understood by considering elements of their structures. As we have considered various families of organic chemicals, we have connected physical properties such as melting and boiling points, and solubility, to the polarity of molecules and other elements of their structure.
Similarly, chemical reactivity can also be related to organic families, with certain characteristic behaviour of substances aligning with these categories. Characteristic reaction patterns include such examples as “substitution at the carbonyl” or “addition across a double bond.”
As with the patterns that exist for physical properties, the patterns that exist for chemical reactivity also have underlying explanations. Reactions, after all, require molecules to interact with one another, and those interactions will not be entirely random. For a reaction between two chemical species to occur, the following must happen:
- The species need to collide
- When they do, they need to be in a somewhat specific orientation, and
- They must have adequate energy when the collision occurs to induce changes in bonding
The so-called ‘productive collisions’ that result in reactions are more likely under certain conditions: higher concentrations of reactants, for instance, or higher temperatures which correspond with faster molecular motion (and harder collisions).
Chemists often use a form of mental model called a “reaction mechanism” to imagine the specific interactions that occur between reacting substances. In a mechanism, oppositely charged (or partially charged) species will often come together, and like-charges will repel. The stability of species to exist on their own is evaluated so that the mechanism makes sense from that perspective. There are rules for proposing and writing good mechanisms and conventional approaches to doing so, including drawing curved arrows to indicate where areas of higher electron density ‘go’ through a multistep process.
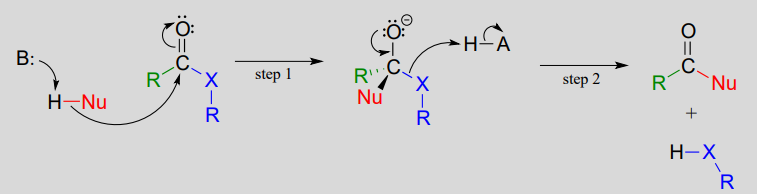
Mechanisms can be supported by experimental evidence, but they are often first built up from considerations of chemical structure that are theoretical e.g. based on symbolic representations and shared understandings of how chemistry works. But no mechanism will be accepted in the face of evidence that is contrary to it.
Many, many reactions are understood both from practical experience and from mechanistic explanations. As an introduction to organic chemistry, the focus in this text will be on just a few example reactions. But hopefully the explanations given here will illuminate the ways that chemical reactivity relates to chemical structure. That is the underlying reason why certain organic families – molecules with specific functional groups – tend to react similarly.
The name ‘functional group’ indicates this, in its most essential sense. Molecules with a certain functional group will function (react) in a certain way.