Using bibliometrics

Scholarly databases such as Scopus, Web of Science and Google Scholar, as well as research analytics tools such as SciVal and InCites can be used to track bibliometrics to measure academic impact.
No single source covers the entirety of your research outputs, so it’s advisable to use more than one when doing citation analysis.
The databases listed below can all be accessed through the RMIT University Library website. They are also linked on the Research Metrics library guide.
Bibliometrics: which database to use?
| Metric name | Description | Database |
|---|---|---|
| Citation count | The citation count is an article-level metric that measures the number of times a publication (usually a journal article or conference paper) has been cited in later publications. There are a number of issues to consider with regard to citation counts. A high count isn’t always an indicator of quality. Some publications are cited because they are examples of poor research, are controversial or are rejoinders to more prominent works. Citations may also result from an author citing their own work. |
Scopus Web of Science Google Scholar |
| h-index | The h-index is an author-level metric designed to measure the impact and productivity of a researcher. The h-index is calculated by the number of papers from an individual’s publication list to have at least the same number of citations. If a researcher has an h-index of 5 then they have at least 5 publications with 5 or more citations. | Scopus Web of Science Google Scholar |
| Citation report | Citation databases allow you to aggregate your output data into a citation report to demonstrate your impact within the academic literature. Statistics provided include: number of items published in each year; number of citations in each year; average citations per item; citation count per item; and, author h-index. | Scopus Web of Science |
| Field Weighted Citation Impact (FWCI) | FWCI is a metric available in Scopus and SciVal. The FWCI is a field-normalised metric that can be applied to an individual publication or group of publications and aims to compare the citations received by a publication or group of publications with the average number of citations received by all other similar publications from the same research field. Also, the FWCI is available for article level metrics in Scopus. | SciVal |
| Category Normalised Citation Impact (CNCI) | CNCI is a metric available in InCites, which analyses publication and citation data from the Web of Science database. The CNCI is similar to the field-weighted citation impact, and benchmarks the impact of an article or group of articles in a particular subject area. | InCites |
Scopus, Web of Science and Google Scholar
Scopus, Web of Science and Google Scholar are citation databases that enable measurement of your h-index and citation counts.
Scopus
Scopus is a comprehensive scientific, medical, technical and social science database produced by Elsevier. Access the Scopus database (login required) to find your h-index, citation counts, and some altmetrics.
- video: Search for an author and view their profile tutorial
- video: How to assess an author's impact tutorial
- guide: Scopus quick reference guide
Web of Science
The Web of Science database is a selective citation index of scholarly publishing covering the most prestigious, high impact research publications in the world. Access the Web of Science database (login required) to find your h-index and citation count.
Google Scholar
Google Scholar comprehensively indexes publications on the web including non-peer-review conferences and other publications. Google Scholar enables researchers to create a profile for themselves once they have publications appearing in the database. This profile allows for an author’s publications to be linked to their profile and displays the author’s h-index and citation counts. Access Google Scholar (login required) to search for a paper's citation count or to find an author's h-index.
Activity
Google Scholar Activity
Access Google Scholar and search for one of your own papers or perhaps a colleague’s or supervisor’s.
Note the citation count. You can see an example of what you are looking for below.
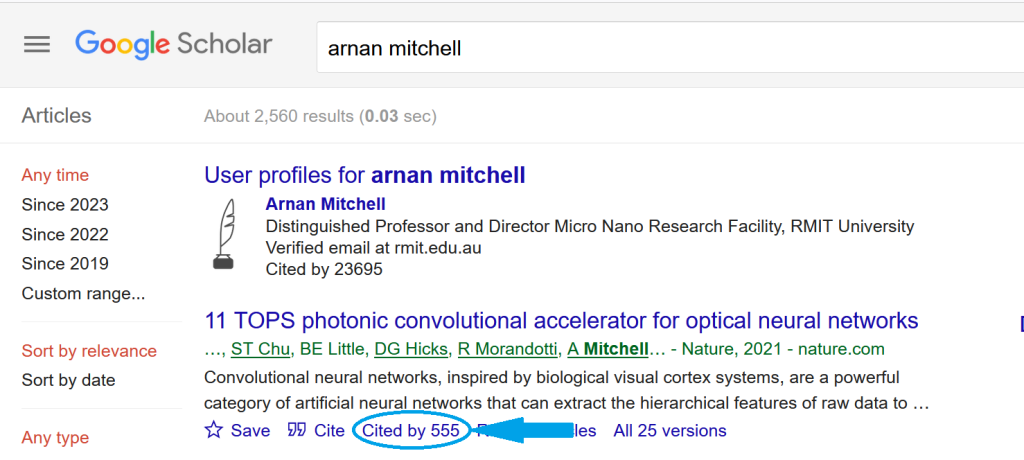
Image: Google and the Google logo are registered trademarks of Google LLC, used with permission.
Web of Science Activity
Now search for the same paper in Web of Science (login required). Compare the Web of Science citation count to that in Google Scholar. Does Web of Science have the same or similar citation count? If different, why might that be?
SciVal and InCites
For a deeper analysis and benchmarking of measures of impact SciVal and InCites are recommended.
SciVal
SciVal is a research analytics tool that can be used to analyse publication and citation data from Scopus.
Access SciVal (login required) to discover your Field-Weighted Citation Impact (FWCI) and more.
- video: SciVal Metrics Guidebook Webinar (55:40 mins)
- guide: Introduction to SciVal
- guide: Research Metrics Guidebook
InCites
InCites is a citation-based evaluation tool that draws its data from the Web of Science database. InCites can provide an analysis of a researcher's work and benchmark output in a field. Access InCites (login required) to discover your CNCI and more.
- video: InCites Essentials (73 mins)
- guide: InCites Benchmarking and Analytics
- guide: InCites Benchmarking & Analytics: Learn the Basics
More information about benchmarking your research is provided in the next chapter.
Research evidence for grants and promotion is a library 'how to' guide on information and tools for describing and capturing evidence of research outputs.
Finally, explore potential issues around relying purely on bibliometrics by watching the following video.
'I am very troubled by the importance of impact factors' Brian Kobilka, Nobel Laureate (1:50 min)
“I am very troubled by the importance of impact factors” Brian Kobilka, Nobel Laureate (1:50 min) by NobelPrizeII (YouTube)

